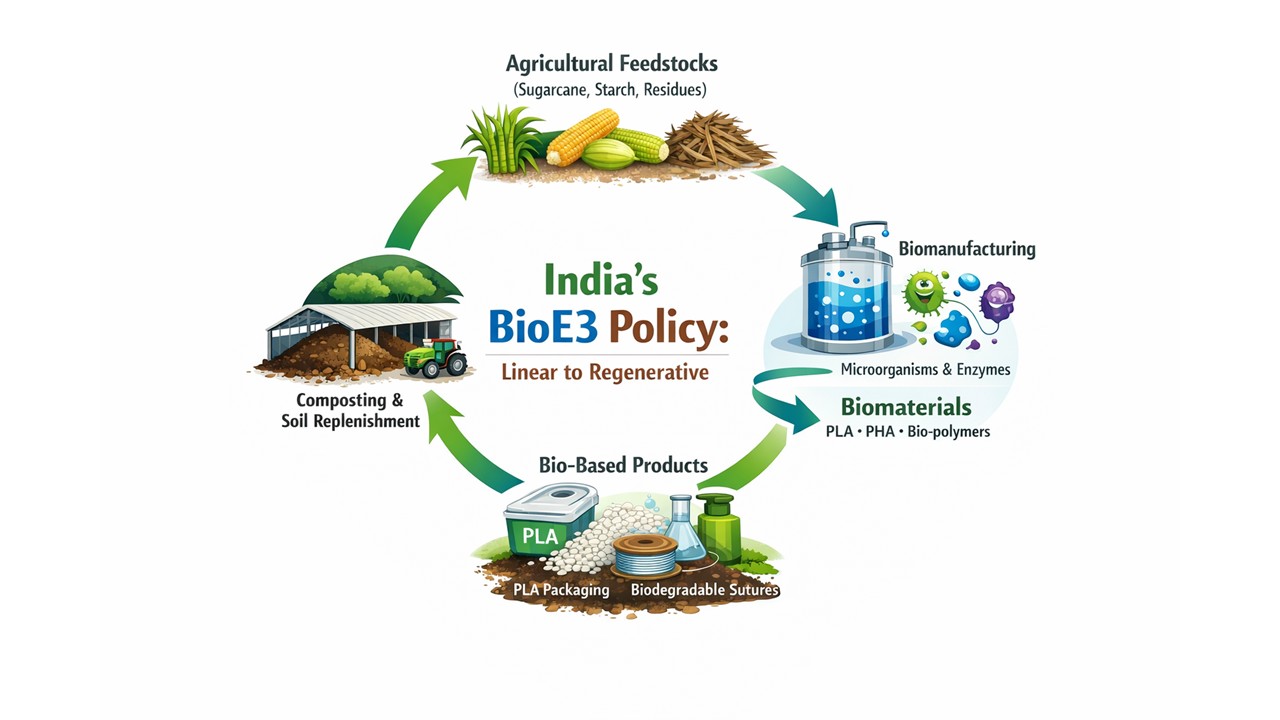
The Union Cabinet approved the BioE3 Policy (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) on 24th August 2024 Policy to give impetus to “High Performance Biomanufacturing.” This policy aims to transform India into a global biotechnology powerhouse by facilitating the sustainable production of bio-based products using advanced living systems₁ ₄. The policy is an initiative of the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science & Technology.

Since its launch policy or BioE3 term has been in news and therefore important for UPSC exam.
High Performance Biomanufacturing
While traditional manufacturing which often relies on petrochemicals and extraction, biomanufacturing uses living systems (such as engineered microbes, plant cells, or animal cells) as “factories” to produce commercially important products₁.
- It integrates advanced biotechnology (like synthetic biology and genome editing) with digital tools (AI and Big Data) to design microbes that can consume biomass or waste and convert them into specific high-value compounds (e.g., bioplastics, enzymes, or medicines)₂.
- The policy aims to shift India from a “consumptive manufacturing” model to a “regenerative manufacturing” model. This means replacing fossil-fuel-based inputs with renewable biological resources, directly supporting India’s Net Zero Carbon targets and the ‘Lifestyle for Environment’ (LiFE) initiative₂.
Key Details & Thematic Sectors
The policy identifies six strategic thematic sectors where biomanufacturing will be prioritized to drive the “Bioeconomy” (Economy), protect the “Environment”, and generate “Employment” (The ‘E3’ framework)₁.
| Thematic Sector | Focus Area | Significance |
| 1. Bio-based Chemicals & Enzymes | Replacing chemical factories with microbial factories. | Reduces industrial toxicity and carbon footprint. |
| 2. Functional Foods & Smart Proteins | Lab-grown meat, plant-based proteins, and nutraceuticals. | Addresses food security and reduces livestock methane emissions. |
| 3. Precision Biotherapeutics | Biologics, gene therapies, and personalized medicine. | Moves beyond generic drugs to high-value advanced healthcare. |
| 4. Climate Resilient Agriculture | Bio-fertilizers, bio-pesticides, and stress-tolerant crops. | Reduces chemical dependency in farming. |
| 5. Carbon Capture & Utilization | Using microbes to “eat” CO₂ and convert it into fuel/chemicals. | Direct climate change mitigation tool. |
| 6. Marine & Space Research | Developing bio-products for extreme environments (e.g., algae for space food). | Futuristic applications and exploring “Blue Economy”. |
Bio-Enablers (Infrastructure Support)
To support these sectors, the policy mandates the creation of shared infrastructure hubs known as Bio-Enablers:
- Bio-AI Hubs: Facilities that combine Artificial Intelligence with biology to simulate and design new microbes faster than traditional trial-and-error methods₂.
- Biofoundries: Large-scale facilities that serve as “design-build-test” factories for testing and scaling up new biological strains before they go to commercial mass production₂.
Sources
1. Press Information Bureau (PIB), Government of India "Cabinet approves BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) Policy"
2. Department of Biotechnology (DBT) "Biomanufacturing Initiative - BioE3"
3. Press Information Bureau (PIB), Government of India "BioE3 Policy to Spearhead Green Growth"
4. India Science, Technology & Innovation Portal "BioE3 Policy Brochure"